Amps to Kilowatts (kW) Conversion Calculator
Enter the current and voltage to convert amps to watts for DC and AC single and three-phase circuits.
On this page:
How to Convert Amps to Kilowatts
To convert amps to kilowatts, you can use the Watt’s Law power formula, which states that I = P ÷ V, where P is the power in watts, I is current in amps, and V is voltage in volts.
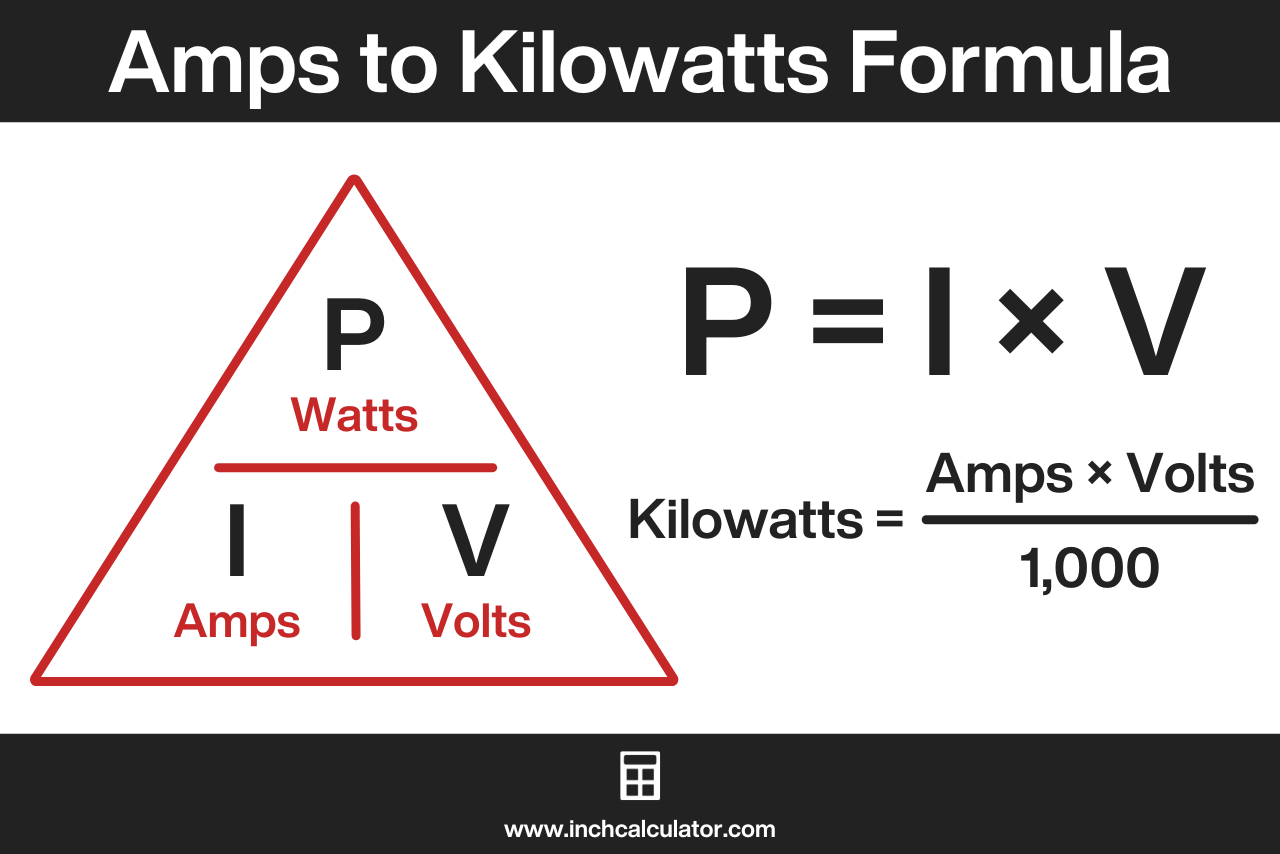
The amps to kilowatts formula derived from the power formula is:[1]
P(kW) = I(A) × V(V) / 1,000
Thus, the power P in kilowatts is equal to the product of the current I in amps and the voltage V in volts, divided by 1,000.
For example, let’s find the power in kilowatts for a circuit with 12 amps of current at 120 volts.
P(kW) = 12 A × 120 V / 1,000
P(kW) = 1,440 W / 1,000
P(kW) = 1.44 kW
Single-Phase AC Circuit Amps to Kilowatts Conversion
Conversion of amps to kilowatts for single-phase alternating current (AC) circuits using the current, RMS voltage, and power factor (PF) can be done with a slightly different formula.
P(kW) = I(A) × V(V) × PF / 1,000
AC electrical power is composed of a real part, expressed in watts (W), and a reactive part, expressed in volt-amps (VA). The magnitude of both real and reactive together is called the apparent power, and the PF gives the ratio of real power to apparent power.[2]
The PF is a property determined by the AC frequency and the amount of inductive or capacitive elements in the circuit.
Thus, the real power P in kilowatts is equal to the current I in amps multiplied by the voltage V in volts multiplied by the power factor PF, divided by 1,000. Try our power factor calculator to get the power factor if needed.
Three-Phase AC Circuit Amps to Kilowatts Conversion
Using Line-to-Line Voltage
The formula to convert amps to kilowatts for three-phase AC circuits where the current, line-to-line RMS voltage, and power factor is known is:[1]
P(kW) = I(A) × VL-L(V) × PF × √3 / 1,000
Thus, the power P in kilowatts is equal to the product of the current I in amps, the line-to-line voltage V in volts, the power factor PF, and the square root of 3, divided by 1,000.
This equation gives you the power for one pair of wires in the three-phase system, but when considering all three pairs, you would need to multiply the result by three.
Using Line-to-Neutral Voltage
The formula to convert amps to kilowatts for three-phase AC circuits where the line-to-neutral RMS voltage is known is:
P(kW) = I(A) × VL-N(V) × PF × 3 / 1,000
Thus, the power P in kilowatts is equal to the product of the current I in amps, the line-to-neutral voltage V in volts, and the power factor PF, multiplied by 3, then divided by 1,000.
This formula gives you the power delivered by all three wires in a three-phase system, but when considering one wire, you will need to divide the result by three.
How to Convert Amps and Ohms to Kilowatts
It is also possible to convert amps to kilowatts using circuit resistance with this formula:
P(kW) = I(A)2 × R(Ω) / 1,000
Thus, the power P in kilowatts is equal to the product of the square of the current I in amps and the resistance R in ohms, divided by 1,000.
You might also be interested in our amps to watts calculator.
Equivalent Amps and Kilowatts at 120V AC
| Current (Amps) | Power (Kilowatts) | RMS Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 amps | 0.12 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 2 amps | 0.24 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 3 amps | 0.36 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 4 amps | 0.48 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 5 amps | 0.6 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 6 amps | 0.72 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 7 amps | .084 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 8 amps | 0.90 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 9 amps | 1.08 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 10 amps | 1.2 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 11 amps | 1.32 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 12 amps | 1.44 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 13 amps | 1.56 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 14 amps | 1.68 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 15 amps | 1.8 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 20 amps | 2.4 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 25 amps | 3 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 30 amps | 3.6 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 35 amps | 4.2 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 40 amps | 4.8 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 45 amps | 5.4 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 50 amps | 6 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 60 amps | 7.2 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 70 amps | 8.4 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 80 amps | 9.6 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 90 amps | 10.8 kilowatts | 120 volts |
| 100 amps | 12 kilowatts | 120 volts |
Equivalent Amps and Kilowatts at 240V AC
| Current (Amps) | Power (Kilowatts) | RMS Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 amps | 0.24 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 2 amps | 0.48 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 3 amps | 0.72 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 4 amps | 0.96 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 5 amps | 1.2 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 6 amps | 1.44 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 7 amps | 1.68 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 8 amps | 1.92 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 9 amps | 2.16 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 10 amps | 2.4 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 11 amps | 2.64 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 12 amps | 2.88 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 13 amps | 3.12 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 14 amps | 3.36 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 15 amps | 3.6 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 20 amps | 4.8 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 25 amps | 6 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 30 amps | 7.2 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 35 amps | 8.4 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 40 amps | 9.6 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 45 amps | 10.8 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 50 amps | 12 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 60 amps | 14.4 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 70 amps | 16.8 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 80 amps | 19.2 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 90 amps | 21.6 kilowatts | 240 volts |
| 100 amps | 24 kilowatts | 240 volts |
References
- Miller, C., Ugly’s Electrical References, 2020 Edition, 2020, Jones & Bartlett Learning, 16-23. https://books.google.com/books?id=1kS8DwAAQBAJ
- Fiore, J., AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach, 2022, 274. http://www.dissidents.com/resources/ACElectricalCircuitAnalysis.pdf





