Voltage Calculator
Use the voltage calculator below to calculate the voltage given the current, power, or resistance.
On this page:
How to Calculate Voltage From Power and Resistance
Voltage is the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit, measured in volts. In a static electric field, it is the measure of the work needed to move a unit of electric charge between two points.
You can calculate the voltage in a circuit using Ohm’s Law, which states that the current through a circuit element is directly proportional to the potential difference applied to it and inversely proportional to the resistance.[1]
Voltage Formula
The Ohm’s Law formula states I = V/R, where I is the current through the circuit (in amperes or amps), V is the potential difference across the circuit (in volts), and R is the resistance of the circuit (in ohms).[2]
By rearranging this formula, you can calculate the voltage by multiplying the current flowing through a circuit by the resistance of the circuit. The formula to calculate voltage is:
V = I × R
Thus, the voltage (or potential difference) V across the circuit is equal to the product of the current I flowing through the circuit and the resistance R of the circuit.
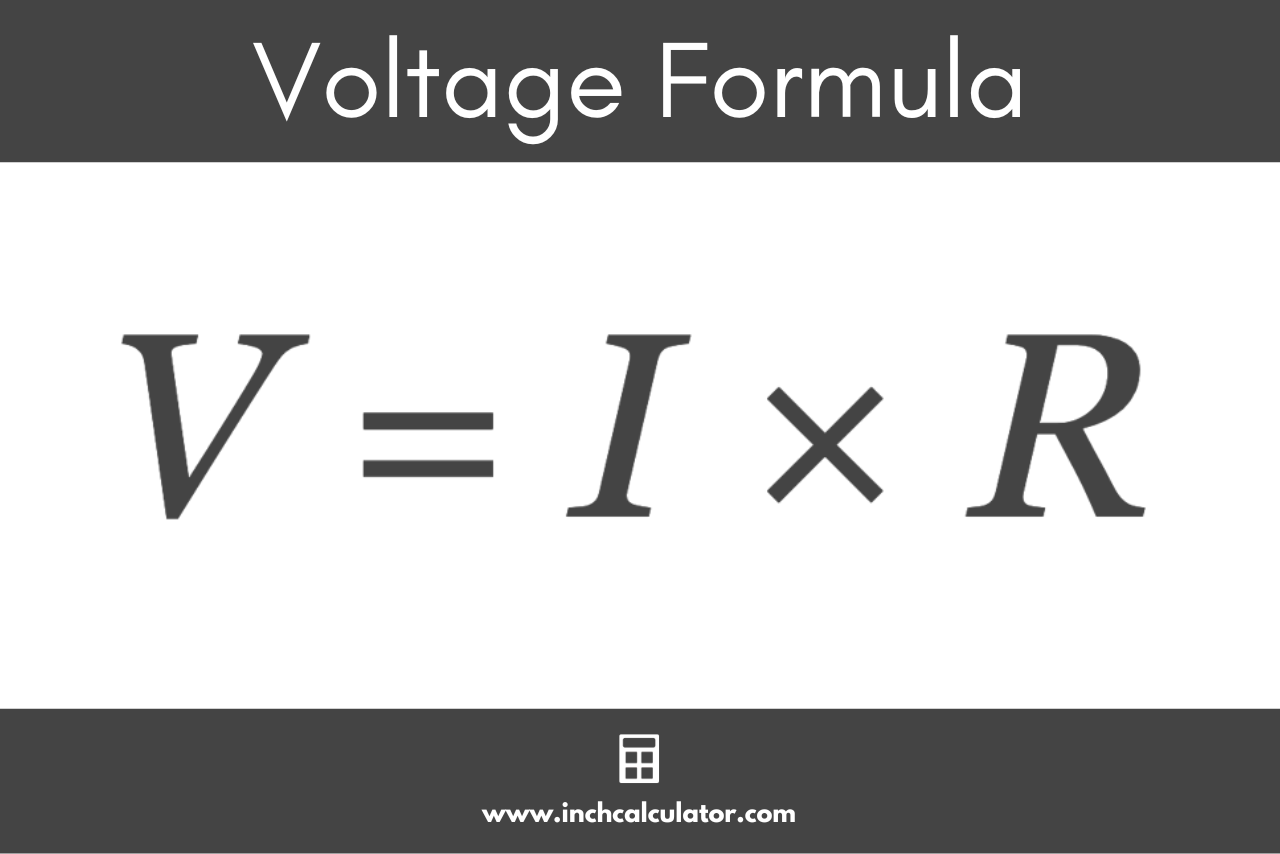
This is the formula that is used to convert amps to volts.
How to Calculate the Voltage From Power
You can also calculate the voltage in a circuit using Watt’s Law power formula. If you know the power in watts drawn through a circuit and the current in amps, the formula to calculate the voltage is:
V = P / I
The voltage (or potential difference across) V of the circuit is equal to the power P drawn through the circuit divided by the current I flowing through the circuit.
This is the formula that is used to convert watts to volts.
References
- Brandon Mitchell, Robert Ekey, Roy McCullough, and William Reitz, A Fan-tastic Quantitative Exploration of Ohm’s Law, https://aapt.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1119/1.5021431
- National Institute of Standards and Technology, Ampere: The Present, https://www.nist.gov/si-redefinition/ampere-present




