Current Calculator – Calculate Amps
Use the current calculator below to calculate amps given the voltage, power, or resistance.
On this page:
How to Calculate Electric Current
In an electrical circuit, current is a measure of the flow of charged particles moving through a conductor. Current is measured in units of amperes (usually referred to as amps).
You can calculate the current flowing through a conductor using Ohm’s Law, which states that the current through a circuit element is directly proportional to the potential difference (also known as voltage) applied to it and inversely proportional to its electrical resistance.[1]
Current Formula
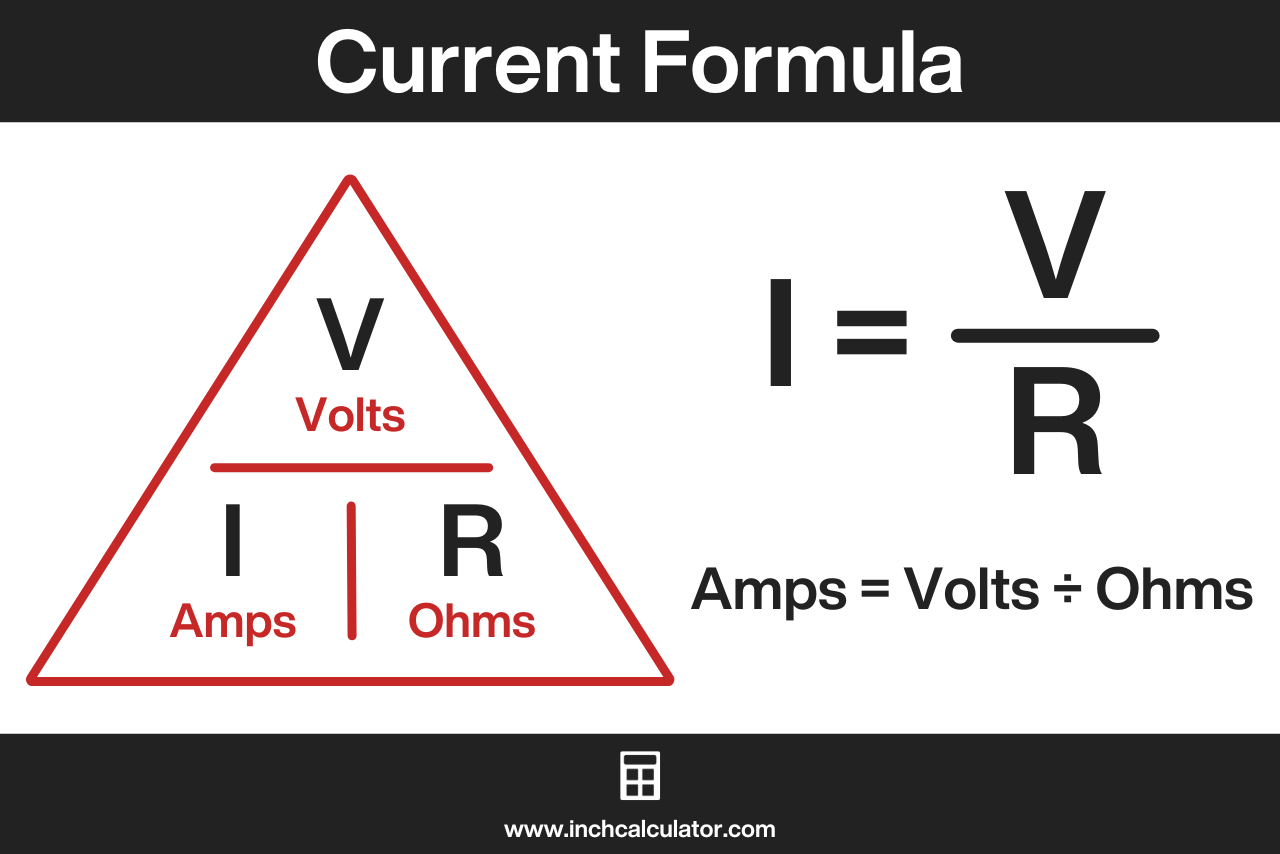
The Ohm’s Law formula to calculate current is I = V/R, where I is the current through the conductor in amps, V is the potential difference across or voltage across the conductor in volts, and R is the resistance of the conductor in ohms.[2]
I = V / R
Thus, the current I flowing through a conductor is equal to the voltage V across the conductor divided by the resistance R of the conductor.
How to Calculate Current From Power
You can also calculate electric current in amps if you know the power drawn from the circuit using the Watt’s Law power formula. The power formula states that the current in amps is equal to the power in watts divided by the voltage.[3]
I(A) = P(W) / V(V)
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the voltage V.
You can use our watts to amps calculator or volts to amps calculator to calculate current in amps, given voltage in volts and power in watts.
How to Calculate Current For AC Circuits
For a single-phase AC circuit given a power factor, you can calculate the current using the following formula.
I(A) = P(W) / V(V) × PF
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of the voltage V and the power factor PF.
You can calculate the power factor using a power factor calculator if needed.
Three-Phase AC Current Formula
To calculate the current for three-phase AC circuits, you need to use a different formula to account for the three phases.
Line-to-Line Voltage Formula
If you know the line-to-line voltage in a three-phase AC circuit, you can use the following formula to calculate the current:[3][4]
I(A) = P(W) / VL-L(V) × PF × √3
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of the line-to-line voltage V in volts, the power factor PF, and the square root of 3.
This formula calculates the current draw for a single pair of wires in three-phase systems. You will need to multiply the result by 3 to calculate the total current for all three pairs.
Line-to-Neutral Voltage Formula
If you know the line-to-neutral voltage in a three-phase AC circuit, you can use the following formula to calculate the current:
I(A) = P(W) / VL-N(V) × PF × 3
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in watts divided by the product of the line-to-neutral voltage V in volts, the power factor PF, and 3.
This formula calculates the total current for all three wires in a three-phase system. You will need to divide the result by 3 to find the current for a single wire in the circuit.
Once you identify how much current you’re working with, you can use our wire ampacity calculator to determine which conductor size is appropriate for the project.
References
- Brandon Mitchell, Robert Ekey, Roy McCullough, and William Reitz, A Fan-tastic Quantitative Exploration of Ohm’s Law, https://aapt.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1119/1.5021431
- National Institute of Standards and Technology, Ampere: The Present, https://www.nist.gov/si-redefinition/ampere-present
- Miller, C., NFPA's Electrical References, National Fire Protection Association, 2004, Jones & Bartlett Learning, 67-75. https://www.google.com/books/edition/NFPA_s_Electrical_References/raUyIi7i-asC
- Miller, C., Ugly’s Electrical References, 2020 Edition, 2020, Jones & Bartlett Learning, 16-23. https://books.google.com/books?id=1kS8DwAAQBAJ




