Celsius to Fahrenheit Converter (°C to °F)
Enter the temperature in degrees Celsius below to convert it to degrees Fahrenheit.
Result in Degrees Fahrenheit:
Do you want to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
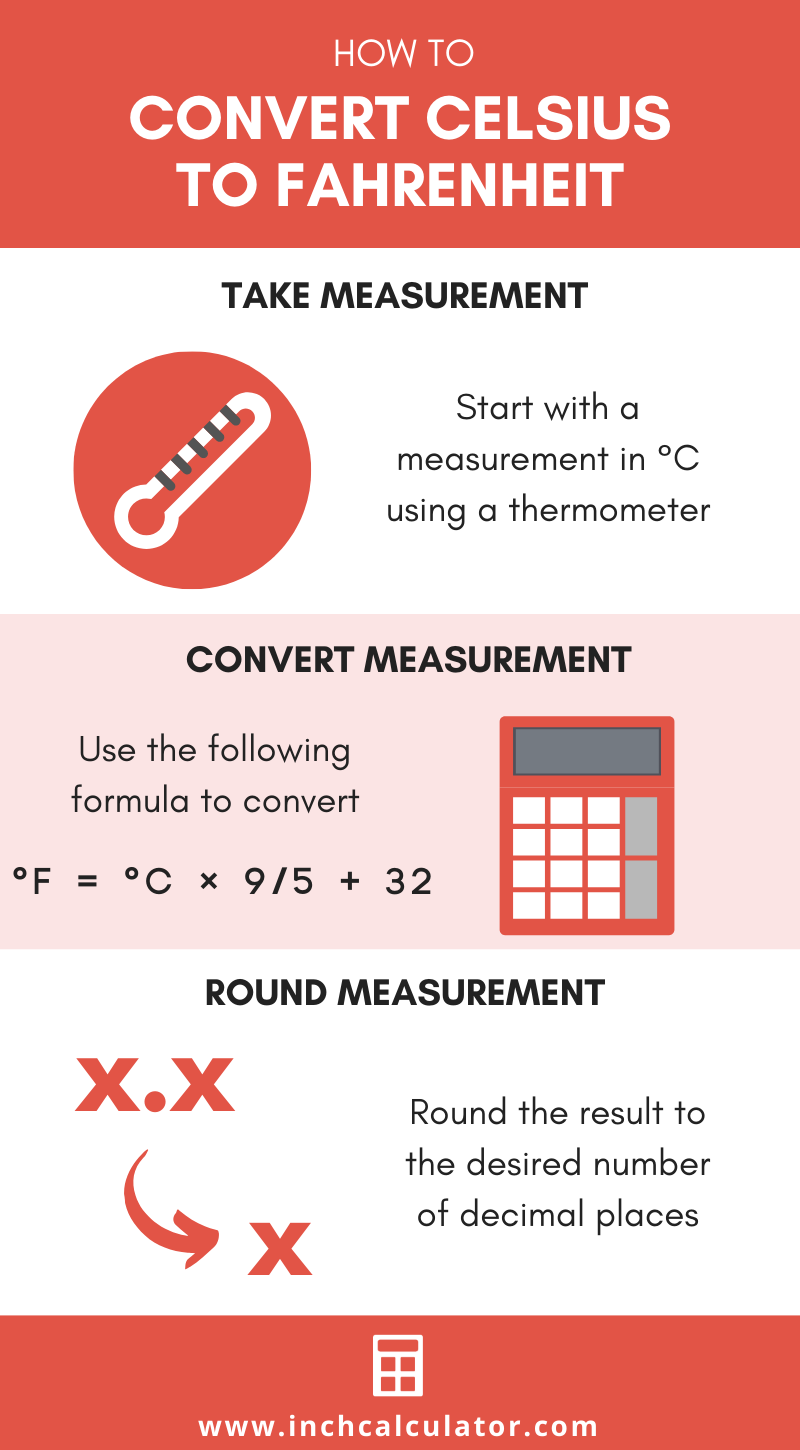
How to Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit
There are a few formulas that you can use to convert a temperature from degrees Celsius to degrees Fahrenheit.
°C to °F Conversion Formula
Convert °C to °F using the widely accepted conversion formula:
°F = °C × 9/5 + 32
The temperature in degrees Fahrenheit is equal to the temperature in degrees Celsius times 9/5, plus 32. Insert the °C temperature measurement in the formula and then solve to find the result.
For example, let's convert 50 °C to °F:
50 °C = 50 × 9/5 + 32
50 °C = 90 + 32
50 °C = 122 °F
Alternate Celsius to Fahrenheit Formula
The National Institute of Standards and Technology defines a simplified formula for the conversion:[1]
°F = (°C × 1.8) + 32
This is a reduced version of the more widely accepted formula shown above.
How to Convert a Temperature Without a Calculator
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit without a calculator, you can use a shortcut method. Multiply the temperature by two, then add 30.
Bear in mind that this is not a precise method; it's a quick shortcut to get a rough conversion when you don't have a calculator handy.
For example, let's use this shortcut to convert 20 °C to Fahrenheit.
Start by multiplying the temperature by 2.
20 °C × 2 = 40
Then, add 30.
40 + 30 = 70
So, 20 °C is approximately 70 °F using this method.
The Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are both used to measure temperature. Read on to learn more about each of them.
Are you converting temperatures or cooking or baking? Try our oven temperature conversion calculator.
Temperature Reference Points In °C and °F
| Temperature | Degrees Celsius | Degrees Fahrenheit |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute Zero | -273.15 °C | -459.67 °F |
| Freezing Point of Water | 0 °C | 32 °F |
| Triple Point of Water | 0.01 °C | 32.018 °F |
| Boiling Point of Water | 100 °C | 212 °F |
| Surface of the Sun | 5,600 °C | 10,100 °F |
Other Common Temperatures
What Is Celsius?
The Celsius temperature scale, also commonly referred to as the centigrade scale, is defined in relation to the kelvin. Specifically, degrees Celsius is equal to kelvins minus 273.15.[1]
The degree Celsius is the SI derived unit for temperature in the metric system. A degree Celsius is sometimes also referred to as a degree centigrade. Celsius can be abbreviated as C; for example, 1 degree Celsius can be written as 1 °C.
Learn more about Celsius.
What Is Fahrenheit?
The Fahrenheit scale is a temperature scale that defines the melting point of water as 32 degrees and the boiling point of water at 212 degrees.[2] There are 180 intervals between 32 °F and 212 °F, each corresponding to one degree.
The degree Fahrenheit is a US customary and imperial unit of temperature. Fahrenheit can be abbreviated as F; for example, 1 degree Fahrenheit can be written as 1 °F.
Learn more about Fahrenheit.
Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion Chart
| Celsius | Fahrenheit |
|---|---|
| -50 °C | -58 °F |
| -40 °C | -40 °F |
| -30 °C | -22 °F |
| -20 °C | -4 °F |
| -17.78 °C | 0 °F |
| -10 °C | 14 °F |
| 0 °C | 32 °F |
| 10 °C | 50 °F |
| 20 °C | 68 °F |
| 30 °C | 86 °F |
| 40 °C | 104 °F |
| 50 °C | 122 °F |
| 60 °C | 140 °F |
| 70 °C | 158 °F |
| 80 °C | 176 °F |
| 90 °C | 194 °F |
| 100 °C | 212 °F |
| 110 °C | 230 °F |
| 120 °C | 248 °F |
| 130 °C | 266 °F |
| 140 °C | 284 °F |
| 150 °C | 302 °F |
| 160 °C | 320 °F |
| 170 °C | 338 °F |
| 180 °C | 356 °F |
| 190 °C | 374 °F |
| 200 °C | 392 °F |
| 300 °C | 572 °F |
| 400 °C | 752 °F |
| 500 °C | 932 °F |
| 600 °C | 1,112 °F |
| 700 °C | 1,292 °F |
| 800 °C | 1,472 °F |
| 900 °C | 1,652 °F |
| 1,000 °C | 1,832 °F |
References
- National Institute of Standards and Technology, SI Units – Temperature, https://www.nist.gov/pml/owm/si-units-temperature
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Weather Service , Fahrenheit, https://w1.weather.gov/glossary/index.php?word=fahrenheit

