Velocity Calculator
Calculate final velocity, initial velocity, acceleration, or time using the velocity calculator below.
Final Velocity:
Final Velocity Formula
Initial Velocity Formula
Acceleration Formula
Time Formula
On this page:
How to Calculate Velocity
Velocity is a fundamental concept in the study of physics, especially in kinematics, the branch of physics that deals with motion. Velocity is the speed of an object in a given direction. It is the rate at which an object moves in a particular direction over time.
There are several methods to calculate velocity, depending on what you know.
How to Calculate Velocity Using Displacement
The most common approach to calculating velocity is by using displacement. Displacement is the overall change in the position of an object, irrespective of the path taken.
It is measured as the straight line distance between the initial and final position of an object. Note that displacement may not be the same as distance, depending on the path taken by the object.
Velocity Formula Given Displacement
If an object travels a certain displacement in a given time duration, then you can calculate the velocity using the formula:
The velocity v is equal to the displacement s divided by the time duration t. This is very similar, though not identical, to the method used to calculate speed. Speed is calculated as distance covered over time, and distance may not be the same as displacement.
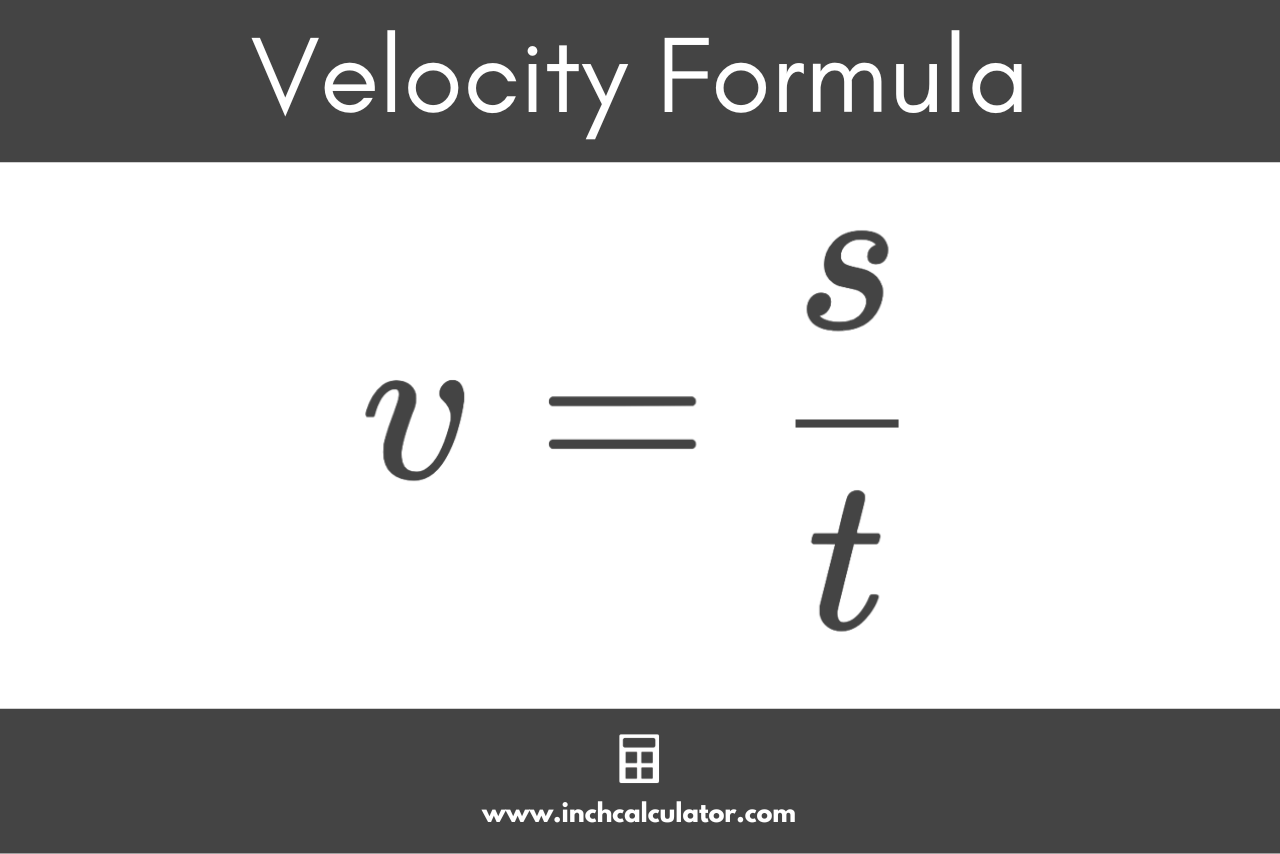
It is important to note that this gives the average velocity over the time period t and not the instantaneous velocity at any given moment in time.
How to Calculate Velocity Using Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. If an object starts from a certain initial velocity and is subjected to a constant acceleration, its velocity will change over time.
Velocity Formula Given Acceleration
The formula to calculate the final velocity is:
The final velocity vt is equal to the initial velocity v0 plus the acceleration a multiplied by the duration of time t.
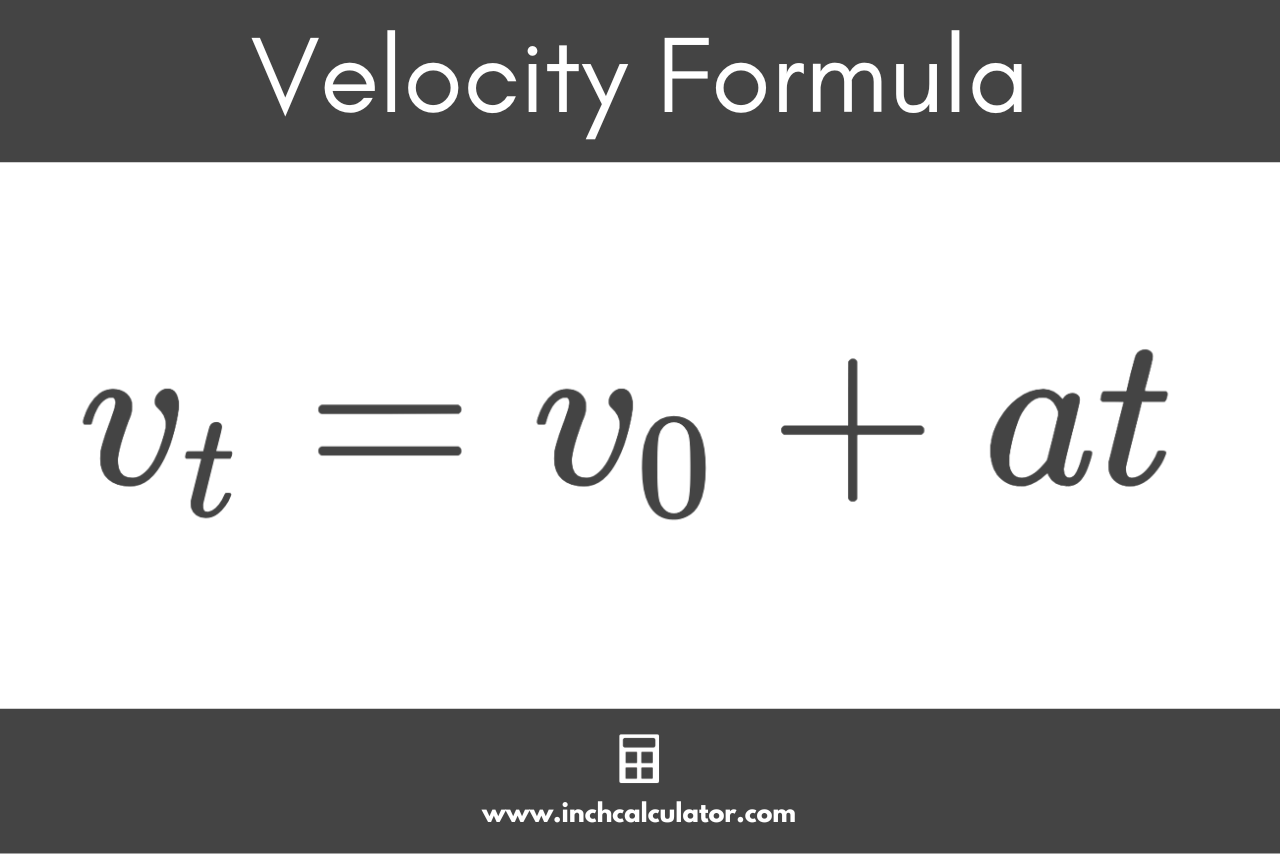
You can use this formula for objects undergoing uniform (constant) acceleration.
It is important to ensure all the units used are consistent. For instance, if velocity is measured in meters per second (m/s) and time in seconds (s), acceleration should be in meters per second squared (m/s²).
How to Calculate Average Velocity
Average velocity is the total displacement divided by the total time taken. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. Unlike speed, which only considers the total distance traveled regardless of direction, average velocity takes the direction of motion into account.
Average Velocity Formula
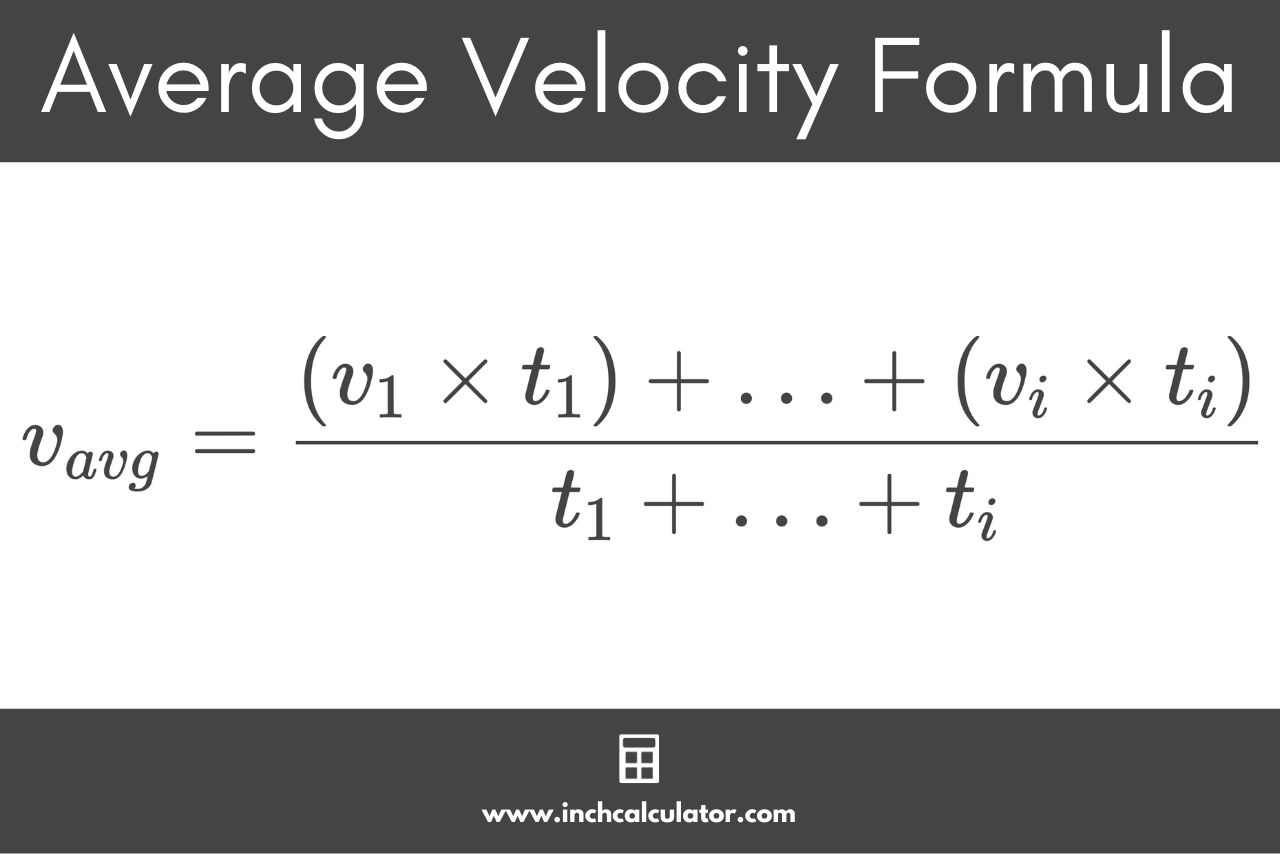
The formula to calculate the average velocity is:
The average velocity vavg is equal to the sum of the products of the velocity vi and time duration ti for each time interval divided by the total time duration. This formula can be used to calculate average velocity when the object is not moving with a constant velocity and the velocity vi is potentially different in each time period ti.
You might also be interested in our terminal velocity calculator.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between velocity and speed?
Speed is a scalar quantity that refers only to how fast an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that refers to how fast and in which direction an object is moving. Velocity has a direction, but speed does not.
What is the difference between velocity and momentum?
While velocity is a vector quantity that describes the rate of change of an object’s position, momentum incorporates the mass of the moving object in addition to its velocity. Momentum is the product of an objects velocity and mass.
If acceleration is zero, what happens to velocity?
If acceleration is zero, it means the object is not speeding up or slowing down. Its velocity is constant. This does not mean the object is at rest unless its velocity is also zero.
Can velocity be negative?
Yes, velocity can be negative, which indicates that the object is moving in a direction opposite to the direction in which it is being measured. For example, a velocity of 6 m/s heading North is the same as a velocity of -6 m/s heading south.
What is the difference between linear velocity and angular velocity?
Linear velocity refers to the rate at which an object moves along a straight path, while angular velocity describes the rate at which an object rotates around a specific axis.
Linear velocity is measured using meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), or miles per hour (mph), while angular velocity is measured in angular rotational units such as radians per second (rad/s) or revolutions per minute (rpm).
Can an object have a constant speed but a changing velocity?
Yes. If an object is moving in a circular path at a constant speed, its direction (and hence velocity) is constantly changing even though its speed remains the same.


