Hertz to Revolutions per Minute Converter
Enter the frequency in hertz below to convert it to revolutions per minute.
Result: Revolutions per Minute
Do you want to convert revolutions per minute to hertz?
On this page:
How to Convert Hertz to Revolutions per Minute
To convert a measurement in hertz to a measurement in revolutions per minute, multiply the frequency by the following conversion ratio: 60 revolutions per minute/hertz.
Since one hertz is equal to 60 revolutions per minute, you can use this simple formula to convert:
revolutions per minute = hertz × 60
The frequency in revolutions per minute is equal to the frequency in hertz multiplied by 60.
For example, here's how to convert 5 hertz to revolutions per minute using the formula above.
revolutions per minute = (5 Hz × 60) = 300 RPM
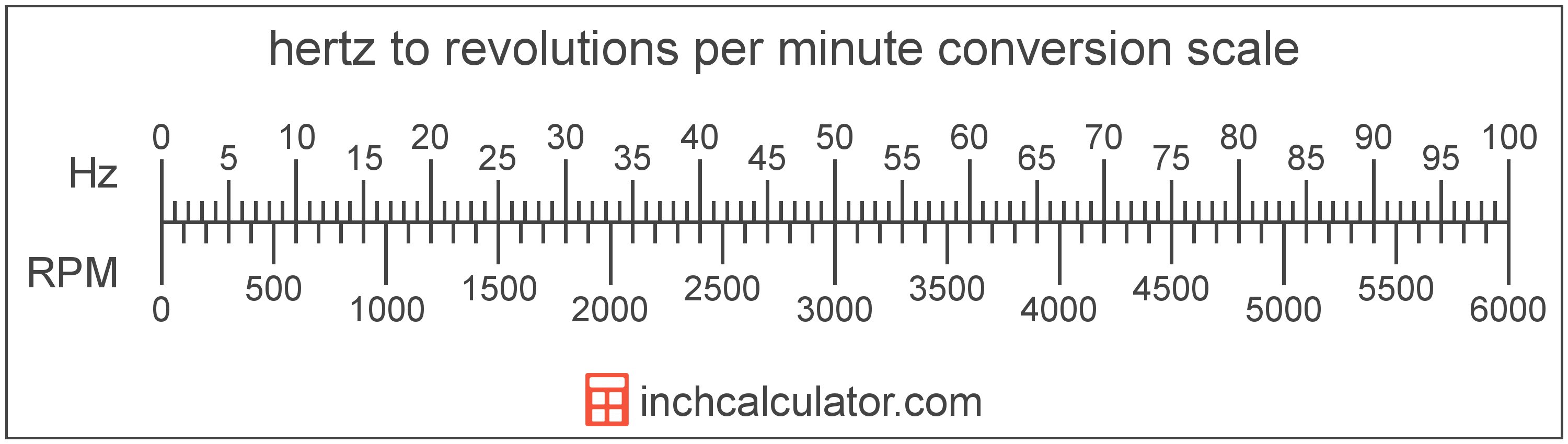
How Many Revolutions per Minute Are in a Hertz?
There are 60 revolutions per minute in a hertz, which is why we use this value in the formula above.
1 Hz = 60 RPM
Hertz and revolutions per minute are both units used to measure frequency. Keep reading to learn more about each unit of measure.
What Is a Hertz?
One hertz is formally defined as the frequency of one cycle per second.[1]
The hertz is the SI derived unit for frequency in the metric system. Hertz can be abbreviated as Hz; for example, 1 hertz can be written as 1 Hz.
Frequency in hertz can be expressed using the formula:
Hz = Cycles / Time in Seconds
Learn more about hertz.
What Are Revolutions per Minute?
Revolutions per minute are a measure of the number of rotations, turns, or revolutions, that an object makes each minute.
Revolutions per minute can be abbreviated as RPM, and are also sometimes abbreviated as rev/min or r/min. For example, 1 revolution per minute can be written as 1 RPM, 1 rev/min, or 1 r/min.
Revolutions per minute can be expressed using the formula:
RPM = Revolutions / Time in Minutes
Learn more about revolutions per minute.
Hertz to Revolution per Minute Conversion Table
| Hertz | Revolutions Per Minute |
|---|---|
| 1 Hz | 60 RPM |
| 2 Hz | 120 RPM |
| 3 Hz | 180 RPM |
| 4 Hz | 240 RPM |
| 5 Hz | 300 RPM |
| 6 Hz | 360 RPM |
| 7 Hz | 420 RPM |
| 8 Hz | 480 RPM |
| 9 Hz | 540 RPM |
| 10 Hz | 600 RPM |
| 11 Hz | 660 RPM |
| 12 Hz | 720 RPM |
| 13 Hz | 780 RPM |
| 14 Hz | 840 RPM |
| 15 Hz | 900 RPM |
| 16 Hz | 960 RPM |
| 17 Hz | 1,020 RPM |
| 18 Hz | 1,080 RPM |
| 19 Hz | 1,140 RPM |
| 20 Hz | 1,200 RPM |
| 21 Hz | 1,260 RPM |
| 22 Hz | 1,320 RPM |
| 23 Hz | 1,380 RPM |
| 24 Hz | 1,440 RPM |
| 25 Hz | 1,500 RPM |
| 26 Hz | 1,560 RPM |
| 27 Hz | 1,620 RPM |
| 28 Hz | 1,680 RPM |
| 29 Hz | 1,740 RPM |
| 30 Hz | 1,800 RPM |
| 31 Hz | 1,860 RPM |
| 32 Hz | 1,920 RPM |
| 33 Hz | 1,980 RPM |
| 34 Hz | 2,040 RPM |
| 35 Hz | 2,100 RPM |
| 36 Hz | 2,160 RPM |
| 37 Hz | 2,220 RPM |
| 38 Hz | 2,280 RPM |
| 39 Hz | 2,340 RPM |
| 40 Hz | 2,400 RPM |
References
- National Institute of Standards and Technology, SI Units - Time, https://www.nist.gov/pml/owm/si-units-time


